The success of
knowledge based systems lies in the quality and extent of the knowledge
available to the system. Acquiring and validating a large croups of
consistent, correlated knowledge is not a trivial problem . This has
give the acquisition process an especially important role in the design
and implementation of these systems. Consequently, effective acquisition
methods have become one of the principal challenges for the AI
researches.
The goals of
this branch of AI are the discovery and development of efficient, cost
effective methods of acquisition. Some important progress has recently
been made in this area with the development of sophisticated editors and
some general concepts related to acquisition and learning.
Definition :-
Knowledge acquisition is the process of adding new knowledge to a
knowledge base and refining or otherwise improving knowledge that was
previously acquired. Acquisition is usually associated with some purpose
such as expanding the capabilities of a system or improving its
performance at some specified task. It is goal oriented creation and
refinement of knowledge . It may consist of facts, rules , concepts,
procedures, heuristics, formulas, relationships, statistics or other
useful information. Sources of this knowledge may include one or more of
the following.
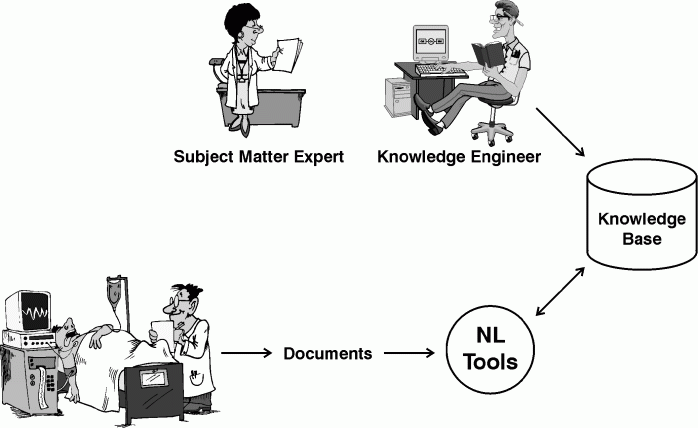
Experts in the domain of interest
Text Books
Technical papers
Databases
Reports
The environment
To be effective, the
newly acquired knowledge should be integrated with existing knowledge in
some meaningful way so that nontrivial inferences can be drawn from the
resultant body of knowledge . the knowledge should, of course, be
accurate, non redundant, consistent(non contradictory ), and fairly
complete in the sense that it is possible to reliably reason about many
of the important conclusions for which the systems was intended.
Types of
learning:- Classification or taxonomy of learning types serves as a
guide in studying or comparing a differences among them. One can develop
learning taxonomies based on the type of knowledge representation used
(predicate calculus , rules, frames), the type of knowledge learned
(concepts, game playing, problem solving), or by the area of
application(medical diagnosis , scheduling , prediction and so on).
The
classification is intuitively more appealing and is one which has become
popular among machine learning researchers . it is independent of the
knowledge domain and the representation scheme is used. It is based on
the type of inference strategy employed or the methods used in the
learning process. The five different learning methods under this
taxonomy are:
Memorization (rote learning)
Direct instruction(by being told)
Analogy
Induction
Deduction
Learning by
memorization is the simplest form of learning. It requires the least5
amount of inference and is accomplished by simply copying the knowledge
in the same form that it will be used directly into the knowledge base.
We use this type of learning when we memorize multiplication tables ,
for example.
A slightly more complex
form of learning is by direct instruction. This type of learning
requires more understanding and inference than role learning since the
knowledge must be transformed into an operational form before being
integrated into the knowledge base. We use this type of learning when a
teacher presents a number of facts directly to us in a well organized
manner.
The third type listed,
analogical learning, is the process of learning an ew concept or
solution through the use of similar known concepts or solutions. We use
this type of learning when solving problems on an examination where
previously learned examples serve as a guide or when we learn to drive a
truck using our knowledge of car driving. We make frewuence use of
analogical learning. This form of learning requires still more inferring
than either of the previous forms, since difficult transformations must
be made between the known and unknown situations. This is a kind of
application of knowledge in a new situation.
The fourth type
of learning is also one that is used frequency by humans. It is a
powerful form of learning which, like analogical learning, also requires
more inferring than the first two methods. This form of learning
requires the use of inductive inference, a form of invalid but useful
inference. We use inductive learning when wed formulate a general
concept after seeing a number of instance or examples of the concept.
For example, we learn the concepts of color sweet taste after
experiencing the sensation associated with several examples of colored
objects or sweet foods.
The final type
of acquisition is deductive learning. It is accomplished through a
sequence of deductive inference steps using known facts. From the known
facts, new facts or relationships are logically derived. Deductive
learning usually requires more inference than the other methods. The
inference method used is, of course , a deductive type, which is a valid
from of inference.
In addition to the above
classification, we will sometimes refer to learning methods as wither
methods or knowledge-rich methods. Weak methods are general purpose
methods in which little or no initial knowledge is available. These
methods are more mechanical than the classical AI knowledge – rich
methods. They often rely on a form of heuristics search in the learning
process.
Bu konuda daha önce hiç bu kadar net bilgi görmemiştim.
ReplyDeleteGerçekten faydalı bilgiler içeriyor, teşekkürler.
ReplyDeleteGerçekten güzel anlatılmış, tebrikler.
ReplyDelete